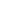
OPAL
Color: multicolored
Moh's hardness scale: 5.5-6

Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica; Because of its amorphous character it is classed as a mineraloid, unlike the other crystalline forms of silica which are classed as minerals. It is deposited at a relatively low temperature and may occur in the fissures of almost any kind of rock, being most commonly found with limonite, sandstone, rhyolite, marl and basalt. Opal is the national gemstone of Australia, which produces 97% of the world's supply.
The internal structure of precious opal makes it diffract light; depending on the conditions in which it formed it can take on many colors. Precious opal ranges from clear through white, gray, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, magenta, rose, pink, slate, olive, brown, and black. Of these hues, the reds against black are the most rare, whereas white and greens are the most common. It varies in optical density from opaque to semi-transparent.
Fire opals are transparent to translucent opals with warm body colors of yellow, orange, orange-yellow or red. They do not usually show any play of color, although occasionally a stone will exhibit bright green flashes. The most famous source of fire opals is the state of Querétaro in Mexico; these opals are commonly called Mexican fire opals.